Exercise User Defined Class 2
Task 1
Type the above definition of a Triangle class
and save in a file.
1. What is the name to be given to this file?
Triangle
2. Compile this file. If you get
any error, it means that you haven’t typed correctly the given codes.
No error detected.
3. After a successful compilation, now try to run. Explain what happened
and why.
Cannot run because there is no main method.
Task 2
Complete
the above Java program and save it in
the same folder where the Triangle class file is located.
1.
Compile this file. If you get any error, it means that you
haven’t typed correctly the given codes.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TriangleDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//create a Scanner object
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// Create a Triangle object.
Triangle triangle = new Triangle();//using java default if takde constructor
// Prompt user to input value for height and base
System.out.println("Enter Height: ");
double height = input.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter base: ");
double base = input.nextDouble();
// Create a Triangle object.
// Triangle triangle = new triangle (height,base);
//Set the height and base
triangle.setHeight(height);
triangle.setBase(base);
//triangle.set(height,base):
// Display the height, base and area
System.out.println("The pyramid's height is "
+ triangle.getHeight());
System.out.println("The pyramid's base is "
+ triangle.getBase());
System.out.println("The pyramid's area is "
+ triangle.getArea());
}
}
2.
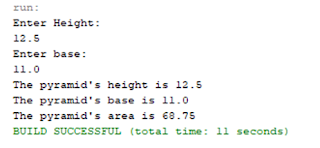
After a successful compilation, now try to run.
What’s the output?
3. List ALL the following items based on the Triangle class:
a) user-defined methods with return value
all the accessor method. Eg: getHeight();
b) user-defined methods with passing-parameters
all mutator method. Eg:
c) accessor methods
triangle.getBase
d) mutator methods
4. Replace the set() method with a constructor. Modify the main()
method.
Task 3
Develop an Employee class which consists of employee ID number, gross pay, state tax and federal tax. You also must create input () method to prompt a user to insert employee ID number, gross pay, state tax and federal tax.Next, develop a Payroll class that consists of two user-defined methods, namely calculateNetPay() and printOutput() methods.
public class PayrollDemo {
public static void
main (String[] args){
//Array of
object Employee
Employee []
arrEmp = new Employee[2];
for (int i=0;
i<arrEmp.length;i++ ){
Employee e
= new Employee();
arrEmp[i]=e;
e.input();
}
for (int i=0;
i<arrEmp.length;i++ ){
Payroll p
= new Payroll();
p.calculateNetPay(arrEmp[i]);
System.out.println("Employee ID "+arrEmp[i].getEmpID());
p.printOutput();
}
// Employee e = new Employee();
// e.input();
//Payroll p =
new Payroll();
//p.calculateNetPay(e);
//
p.printOutput();
}



Comments